One
program; many interfaces
GDE
is a program that
launches other programs. When GDE is starts up, it reads a
file called .GDEmenus, specifiyng a set of programs that GDE can call,
and the menus for setting parameters. BIRCH has .GDEmenus files for
four different data types, resulting in four different GDE interfaces.
GDE - Sequence Data

GDE was specifically designed as a sequence editor. To launch GDE from the command line, type
gde
The File --> Open menu can read three types of files: GDE format, GDE flatfile, and GenBank. Many other sequence formats can be imported using File --> Import Foreign Format.
GDE has several sequence-related functions in the Edit and DNA/RNA menus that are hard coded into the program. In the Edit menu, these include Compress (remove gaps from an alignment) and Reverse (invert the orientation of a sequence, withough complementing). In the DNA/RNA menu, Complement generates the complement, without inverting the orientation. Thus, to create the inverse complement of a sequence, you must use both Reverse AND Complement.
All other functions called by GDE are added using the .GDEmenus file (see next page).
The GDE flat file format was designed to allow "sequences" to contain plain text. This was originally intended as a commenting feature, but we can take advantage of it for reading many kinds of text data. Three additional GDE interfaces exploiting this feature are described below.
dGDE - List Data (eg. Accession numbers, TaxID numbers, GI numbers)
The dGDE interface provides a set of menus for SeqHound web services. SeqHound is a data warehouse integrating dozens of databases into a single database. Most SeqHound functions take a number or identifier as input, and return a number or identifier as output. In other cases, data (eg. sequences, species names, Gene Ontology names) are returned.
To launch dGDE, type
dgde
List data can be saved and read in GDE format using the File --> Open menu. Alternatively, files containing raw lists with one item per line can be read using File --> Import Namefile.
In the example below, the TaxID number for the genus Brassica (3705) was used to retrieve all taxonomy progeny, in this case, all Brassica species, to the list 3705.taxid. 3705.taxid was used to call 'Get Name from TaxID to retrieve a list of species names corresponding to these TaxID numbers. 3705.taxid was next used as input for 'Get DNA/protein from Taxid' to retrieve the GI numbers for all DNA sequences from each species. Note that the sequences from each species each appear as a separate list in the new dGDE window.

mGDE - Marker Data
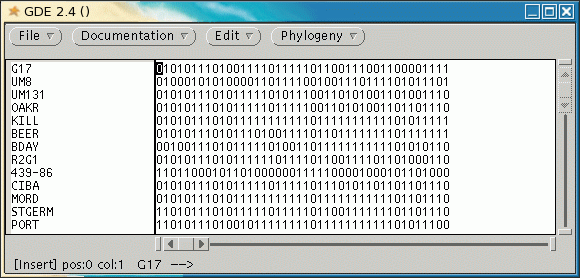
mGDE is a GDE interface specialized for molecular marker data.
To launch mGDE, type
mgde
At present, mGDE can only read marker data in Phylip Discrete Data format. This format takes 1's and 0's as markers, usually representing presence of absence of a marker band. To read in discrete data, choose File --> Import Phylip Discrete Data.
tGDE - Phylogenetic Tree Data
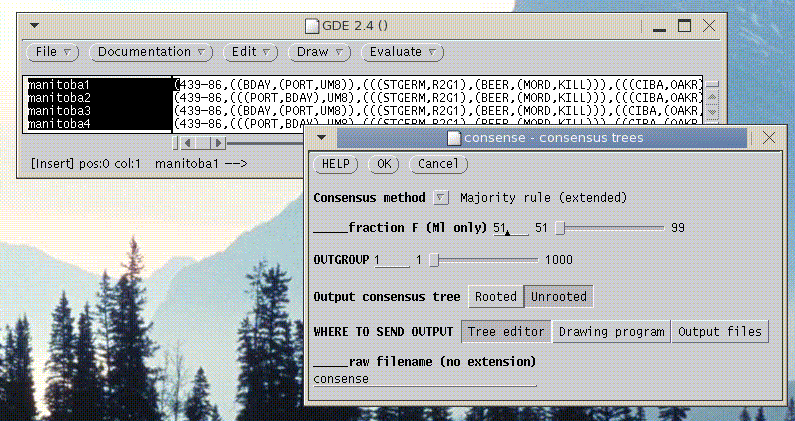
tGDE is a GDE interface specialized for phylogenetic tree data. To launch tGDE type
tgde
At present, tGDE can only read trees in Phylip tree format. To read in a file containing trees, choose File --> Import Trees.
|
|
    |
|